Our WAF has a new user interface – for more intuitive and efficient use. Learn more
Home>
mTLS
02
How does mTLS work?
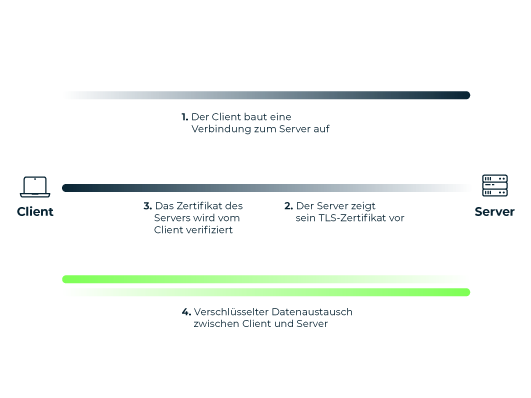
In standard TLS connections, which are used to secure online banking, for example, only the server has a key pair consisting of a public and private key. The client merely verifies the server's TLS certificate to exchange data via the encrypted connection.
03
How are the certificates provided?
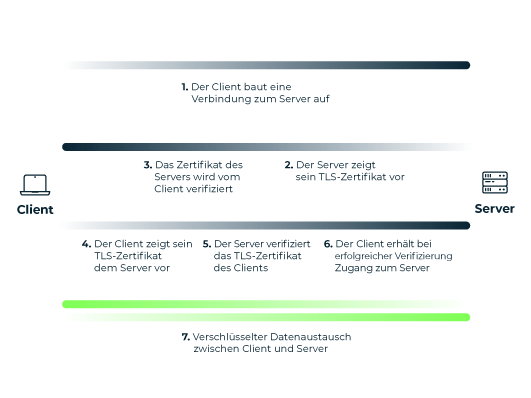
The certificates required for mutual authentication are provided by a central Certificate Authority (CA). In an enterprise context the CA is usually operated by the respective company itself. For this, the company requires a "root" TLS certificate. In contrast to conventional TLS connections, as are common on the free Internet, no external certification authority is therefore required here – the company can create the root certificate itself.
Myra's Security-as-a-Service solutions support the use of client certificates using mTLS. This enables customers to secure particularly critical web content with an additional layer of protection.
About the author
Stefan Bordel
Senior Editor
About the author
Stefan Bordel has been working as an editor and technical writer at Myra Security since 2020. In this role, he is responsible for creating and maintaining website content, reports, whitepapers, social media content and documentation. This role allows him to bring his extensive experience in IT journalism and technical knowledge to an innovative cyber security company. Stefan previously worked at Ebner Verlag (formerly Neue Mediengesellschaft Ulm) for 7 years and joined the online editorial team at com! professional after working for Telecom Handel. He gained his first journalistic experience during various internships, including at the IT website Chip Online. As a passionate Linux user, he follows the IT scene closely, both privately and professionally.