Discover how Myra combines digital sovereignty and cyber resilience.
Home>
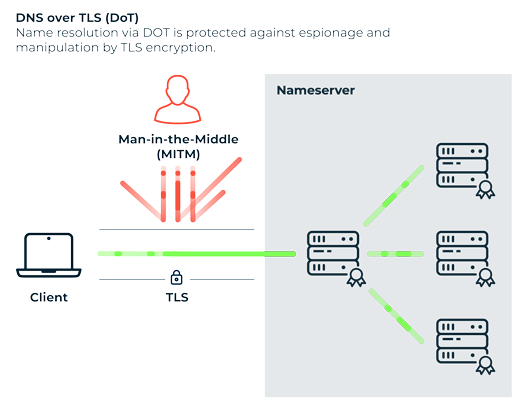
DNS over TLS
03
What does DNS over TLS protect against?
The threat potential of DNS-based attacks was demonstrated in 2019, for example, when the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) issued an urgent warning about a global DNS hijacking campaign. The attack affected dozens of domains belonging to government, telecommunications and Internet infrastructure organizations in Europe, North America, North Africa and the Middle East. Actors with a state background are believed to have been behind the attacks, primarily pursuing political goals.
05
What are the alternatives to DNS over TLS?
DoT is not the only way to protect DNS queries. Over the years, a whole range of standards and extensions have evolved to authenticate and/or encrypt DNS. Here is a selection of the most common solutions at a glance:
DNS over HTTPS
DNS over HTTPS (DoH) is currently one of the most common solutions for DNS encryption, alongside DoT. With DoH, DNS queries and responses are sent using the secure website protocol HTTPS via port 443. This makes the transmissions indistinguishable from conventional website traffic, which prevents targeted blocking of the technology, for example by the network operator. Compared to conventional DNS name resolution, DoH is less performant. DoH was standardized by the IETF in 2018 as RFC 8484.
DNS over QUIC
DNS over QUIC (DoQ) is a novel protocol currently being standardized by the IETF. DoQ aims to combine the advantages of encrypted name resolution with short latency times. For high-performance data transfer, DoQ uses the new QUIC protocol, which is also used in HTTP/3 and relies on TLS 1.3 for security.
DNSCrypt
DNSCrypt is also a protocol that is used for encryption, authentication, and optionally anonymization of communication between the DNS client and the DNS resolver. The data traffic to the DNS resolver is safeguarded via asymmetric encryption using Curve25519. By default, DNSCrypt uses port 443. To anonymize DNS queries, DNSCrypt can be extended with Anonymized DNS technology, which is also compatible with the other encrypted protocols, but which DNSCrypt claims is the easiest and most efficient to implement.
DNSSEC
DNSSEC is a security extension that provides source authentication during name resolution. The technology can be used to validate the integrity of web servers and the connections established with them. This ensures that a specific domain is in fact assigned to the correct web server. Sabotage attempts can thus be detected and countered. DNSSEC can also be used to secure the integrity of digital communication via e-mail or VoIP. Unlike DoT, DoH, or DNSCrypt, DNSSEC does not encrypt the name resolution; the focus here is solely on integrity checking to rule out any damaging manipulation.
Want to learn more about our solutions, use cases and best practices for attack defense? In our download area you will find product sheets, fact sheets, white papers and case studies.
About the author
Björn Greif
Senior Editor
About the author
Björn started his career as an editor at the IT news portal ZDNet in 2006. 10 years and exactly 12,693 articles later, he joined the German start-up Cliqz to campaign for more privacy and data protection on the web. It was then only a small step from data protection to IT security: Björn has been writing about the latest trends and developments in the world of cybersecurity at Myra since 2020.