Discover how Myra combines digital sovereignty and cyber resilience.
Home>
Blockchain
05
What are the advantages of blockchain?
Compared to classic databases or cloud architectures, blockchain-based solutions offer a number of advantages. The most important attributes of the technology include:
Availability & reliability:
Blockchain solutions have a number of advantages over centralized systems. The architectural structure alone ensures a high level of reliability. Whereas conventional databases are operated on central servers, which in turn clients access to query and process the data, management of the data is shared in a blockchain network. If a technical failure occurs at one node, the data is still available across all other instances. In contrast, server problems in centralized architectures usually cause limited availability, depending on the degree of redundancy.
Secure transfer of values:
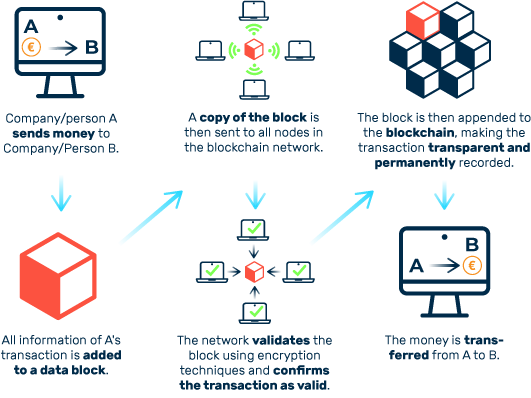
Transactions in the blockchain are technologically verified and recorded. This means that transfers of values and data can be transparently traced and recorded in a tamper-proof manner for all entities involved in the network.
No intermediaries:
All transactions in the network are peer-to-peer (P2P) with no need for intermediaries such as banks, notaries, or governments. By dispensing with trust-building intermediaries, business processes can be highly automated, resulting in savings of both time and money. Therefore, blockchain technology has great potential in logistics for automated supply chains and the like.
06
What are the drawbacks of blockchain?
Blockchain is also not free of disadvantages and problematic properties, especially since many blockchain solutions are still struggling with teething problems. The biggest shortcomings of blockchain technology are:
Resource requirements:
The proof-of-work concept, in particular, requires vast amounts of computing resources and power. For example, the average power consumption of a single bitcoin transaction in 2020 was 741 kilowatt hours. By comparison: The same amount of energy can be used to make nearly 500,000 Visa transactions (source: Statista). In addition, the cumulative storage requirements of branched blockchain databases are many times higher than those of centralized server systems.
Slow:
The high technological overhead for cryptographically verifying transactions makes blockchain solutions comparatively slow. By direct comparison, centralized cloud architectures work faster and can handle far more transactions.
Lack of practical feasibility:
Even though the high potential of blockchain-based solutions is undisputed, the technology is still in its infancy. There is a lack of standardization and clarity. The BSI, for example, criticizes the confusing abundance of available solutions, which makes it difficult to select a specific product with any certainty. Practical implementations are only available for a few companies and industries, and connecting legacy systems poses problems. Moreover, IT specialists with the requisite blockchain skills are in short supply in the competitive labor market.
07
Where blockchain is used?
Numerous blockchain-based solutions leverage the characteristics of decentralized data processing. Blockchain solutions unlock the greatest potential when they build directly on the positive attributes of the technology. Among the best-known applications are:
Cryptocurrencies
The most prominent example of blockchain is the bitcoin cryptocurrency, which is regularly featured in the headlines with wild price fluctuations. Due to extreme volatility, bitcoin and most other blockchain tokens are unsuitable for normal payment transactions. Much more, cryptocurrencies currently serve as speculative investments for risk-taking investors.
Smart contracts
Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain is currently being used in logistics for the automated tracking of supply chains and the processing of customs and tax formalities via smart contracts. Initial pilot projects by international shipping companies and seaports have already been underway for several years. Using blockchain can make the required trade documentation more transparent, faster, and more cost-efficient. Documents are transmitted, validated, and approved electronically and automatically between the individual trading partners and the responsible customs authorities.
E-health
The digital corona vaccination certificate also relies on blockchain. The solution is designed to enable citizens to electronically share their vaccination status for things such as attending events or for checking in at hotels. The vaccination data and personal details such as name, address, and ID number are encrypted and stored on a total of five blockchains. For citizens, however, only the associated QR code is relevant, which is used to compare the data. The code can be printed out or used in a software-based wallet on a smartphone.
Want to learn more about our solutions, use cases and best practices for attack defense? In our download area you will find product sheets, fact sheets, white papers and case studies.
About the author
Björn Greif
Senior Editor
About the author
Björn started his career as an editor at the IT news portal ZDNet in 2006. 10 years and exactly 12,693 articles later, he joined the German start-up Cliqz to campaign for more privacy and data protection on the web. It was then only a small step from data protection to IT security: Björn has been writing about the latest trends and developments in the world of cybersecurity at Myra since 2020.